Type II vs. Type III Anodize
Anodizing is one of the most popular metal finishing techniques for aluminum parts. It typically consists of building a thin coating on the part to enhance its durability, hardness, and abrasion resistance. This coating, much harder than a painted surface, tends to last longer and won't peel or chip. Other advantages of anodizing include enhancing part aesthetics with various colors, corrosion resistance properties, and the minimal environmental impact the method offers.
If you're curious about the similarities and differences between Type II and Type III anodizing, you've come to the right place. Which would you rather have: a Type II conventional sulfuric acid anodize that can be decorated in nearly any color or a Type III hard coat anodize that will result in a denser, thicker, and more abrasion-resistant coating? Let’s take a closer look at these
anodizing methods before you answer that question.
Type II Anodizing
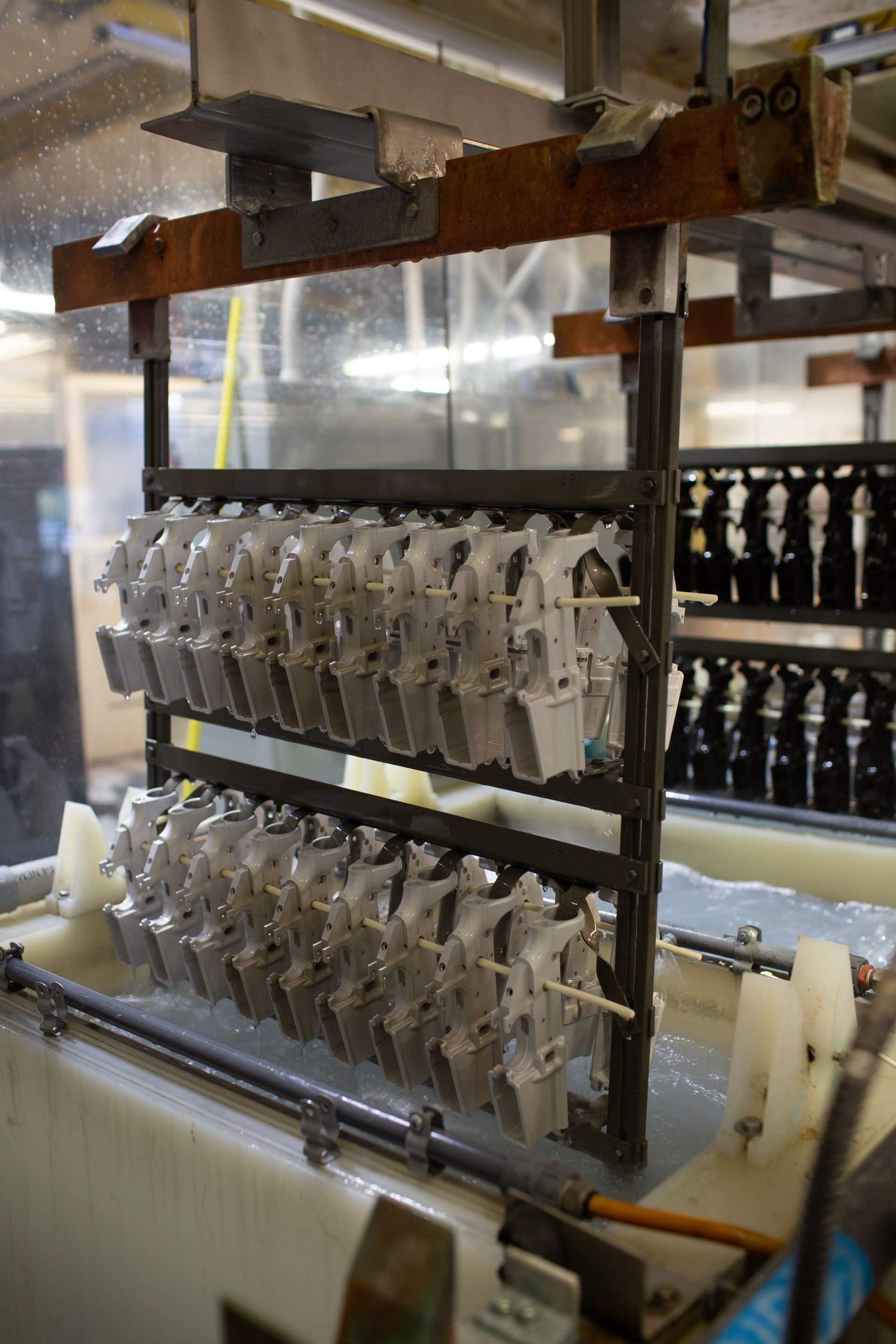
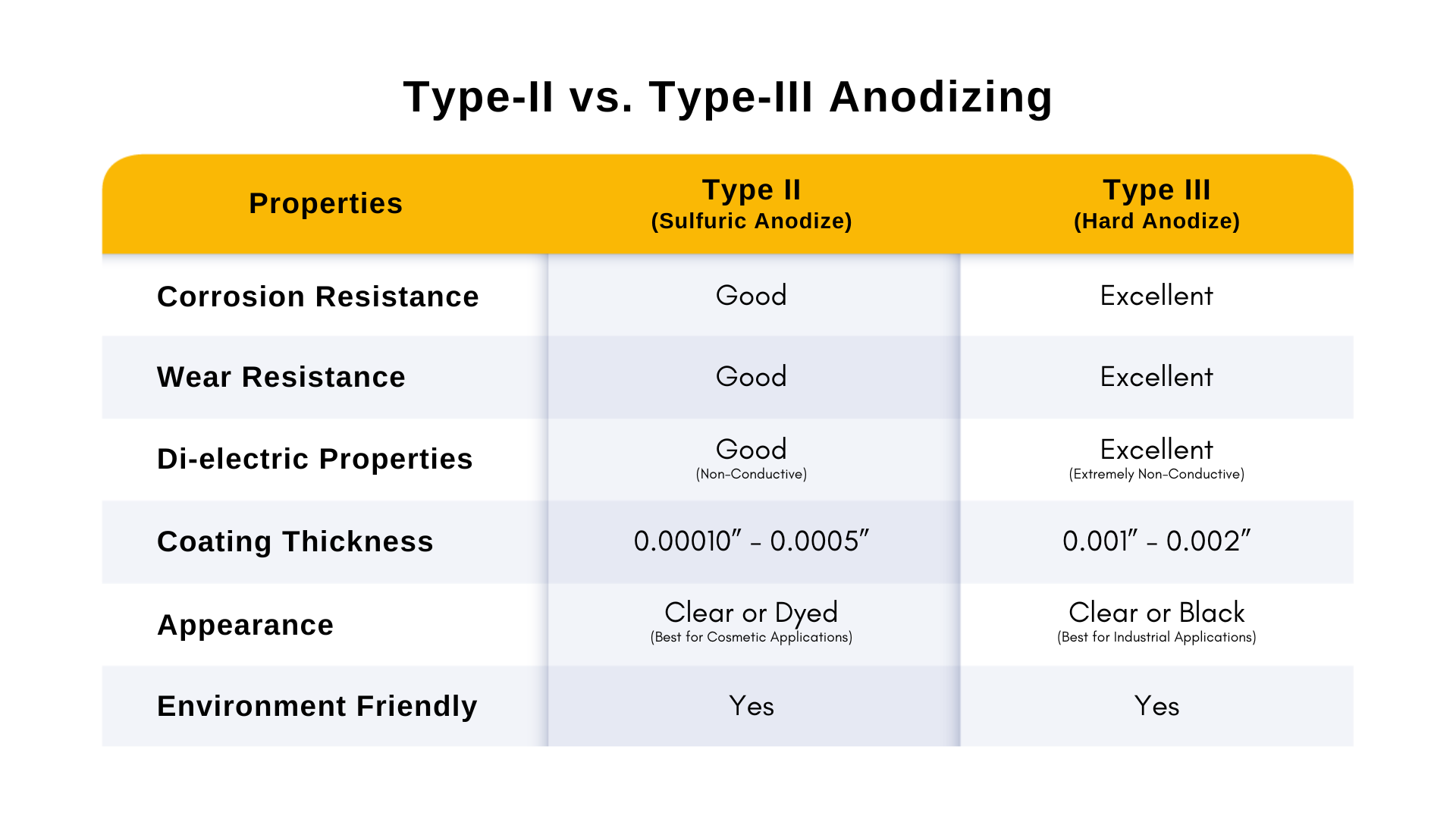
Type II anodizing, also know as sulfuric acid anodizing, typically with a thickness between 0.00010” and 0.0005” inches. Commonly derived from the military standard spec Mil-A-8625, Type II anodizing consists of artificially building an oxide coating in a sulfuric acid bath at around 70 degrees Fahrenheit.
Type II Anodizing Benefits
Type II anodizing is renowned for its versatility and economical approach, making it a preferred choice for many industries. One of the significant benefits of Type II anodizing is its ability to offer enhanced corrosion protection on aluminum, guarding against environmental exposure and increasing the longevity of the parts.
Another notable benefit is Type II anodizing can improve part aesthetics by allowing the part to be dyed in various colors, providing design flexibility to meet specific needs. This is especially valuable in industries like automotive and aerospace, where aesthetic appeal is often as important as functionality.
Moreover, Type II anodizing is an economical and affordable practice, especially when compared to the more expensive Type III anodizing. This cost-effectiveness makes it a practical choice for part runs in industries where budget considerations are paramount.
Type II Common Applications
Type II anodizing, with its versatile anodic coating, is commonly applied in several industries due to its economical nature.
- Aerospace - Used to protect aerospace components from environmental factors like moisture and chemicals
- Automotive - Enhances the longevity and aesthetics of vehicle parts
- Medical - Applied to medical equipment due to its biocompatibility and aesthetic appeal
- Semiconductor - Used in various components of semiconductor manufacturing equipment due to its corrosion resistance and the ability to maintain a high level of purity during semiconductor processing
- Cosmetics - employed in cosmetic product packaging to create visually appealing and corrosion-resistant finishes for items like perfume bottles and jewelry
Type III Anodizing
Compared to Type II anodizing, the coating applied via Type III anodizing is usually thicker, done at a lower temperature, and more expensive. However, there are benefits to Type III anodizing, such as a thicker coating (typically between 0.001 and 0.002 inches) that tends to be more durable and abrasion resistant. It also has greater thermal shock resistance than Type II. This means it can tolerate significant impacts from sound or other damaging sources without failing.
Type III Anodizing Benefits
One of the key benefits of Type III anodizing is its superior abrasion and wear resistance, ensuring the longevity of components in industries like firearms and the military, where equipment is often exposed to extreme conditions.
Type III anodizing, also known as
hard coat anodizing, also offers excellent corrosion resistance, similar to Type II, but with enhanced durability, making it suitable for applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as aerospace components.
Another advantage is its availability in dyed and non-dyed formats, allowing for improved aesthetics and design flexibility. This is particularly beneficial in the electronics industry, where it also acts as an effective electrical insulator.
Type III Common Applications
Type III anodizing is prized for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and dimensional stability. These properties make it indispensable in industries where durability, longevity, and performance are critical factors. While it may be costlier and add more weight compared to Type II anodizing, its superior properties justify its use in applications where toughness and protection against wear and corrosion are paramount:
- Aerospace - Makes components strong enough to handle harsh conditions and meet the industry's high standards
- Firearms and Military Equipment - This type of anodizing is chosen for its top-notch wear and corrosion resistance, essential for keeping equipment in good shape in extreme situations
- Electronics - Provides electrical insulation and helps components last longer
- Marine - Protects against the corrosive marine environment
If you’re unsure which coating type is right for your application, call Light Metals and Coloring, and we’d be happy to assist you in the right direction.
How To Choose Between Type II & Type III Anodizing
If you want your aluminum components to stand out and withstand the environments they were designed for (and look really great) then you'll need to get it anodized.
For more information on the differences and similarities between Type II and Type III anodizing, reach out to Light Metals Coloring. As metal finishing experts, we'll match your next part run with the best process. Contact us today for more information and to learn which
anodized aluminum technique is best for your part.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary difference between Type II and Type III anodizing?
The main difference lies in the thickness and durability of the coating. Type II anodizing creates a thinner, versatile coating (0.0001”–0.0005”), while Type III, also known as hard coat anodizing, produces a thicker, more abrasion-resistant coating (0.001”–0.002”) suitable for extreme conditions.
Which anodizing type is better for corrosion resistance?
Both Type II and Type III anodizing offer excellent corrosion resistance. However, Type III provides enhanced durability and is better suited for harsh environmental conditions or applications requiring maximum protection against wear and tear.
Can Type II and Type III anodizing be dyed in different colors?
Yes, both types can be dyed. Type II anodizing is commonly used for decorative purposes due to its wide color options, while Type III can also be dyed but is often left non-dyed for industrial and functional applications. Learn more about anodized aluminum colors and our coloring process.
Which industries commonly use Type II and Type III anodizing?
Type II is widely used in aerospace, automotive, medical, and cosmetics industries for its cost-effectiveness and design flexibility. Type III is favored in aerospace, firearms, military, and electronics industries due to its superior abrasion resistance and thermal shock properties.
How do I choose the right type of anodizing for my project?
The choice depends on your application requirements. For decorative, lightweight, and cost-effective solutions, Type II is ideal. For heavy-duty, wear-resistant applications exposed to extreme conditions, Type III is the better choice. Contact Light Metals Coloring for expert guidance in selecting the best anodizing method for your specific needs.
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.