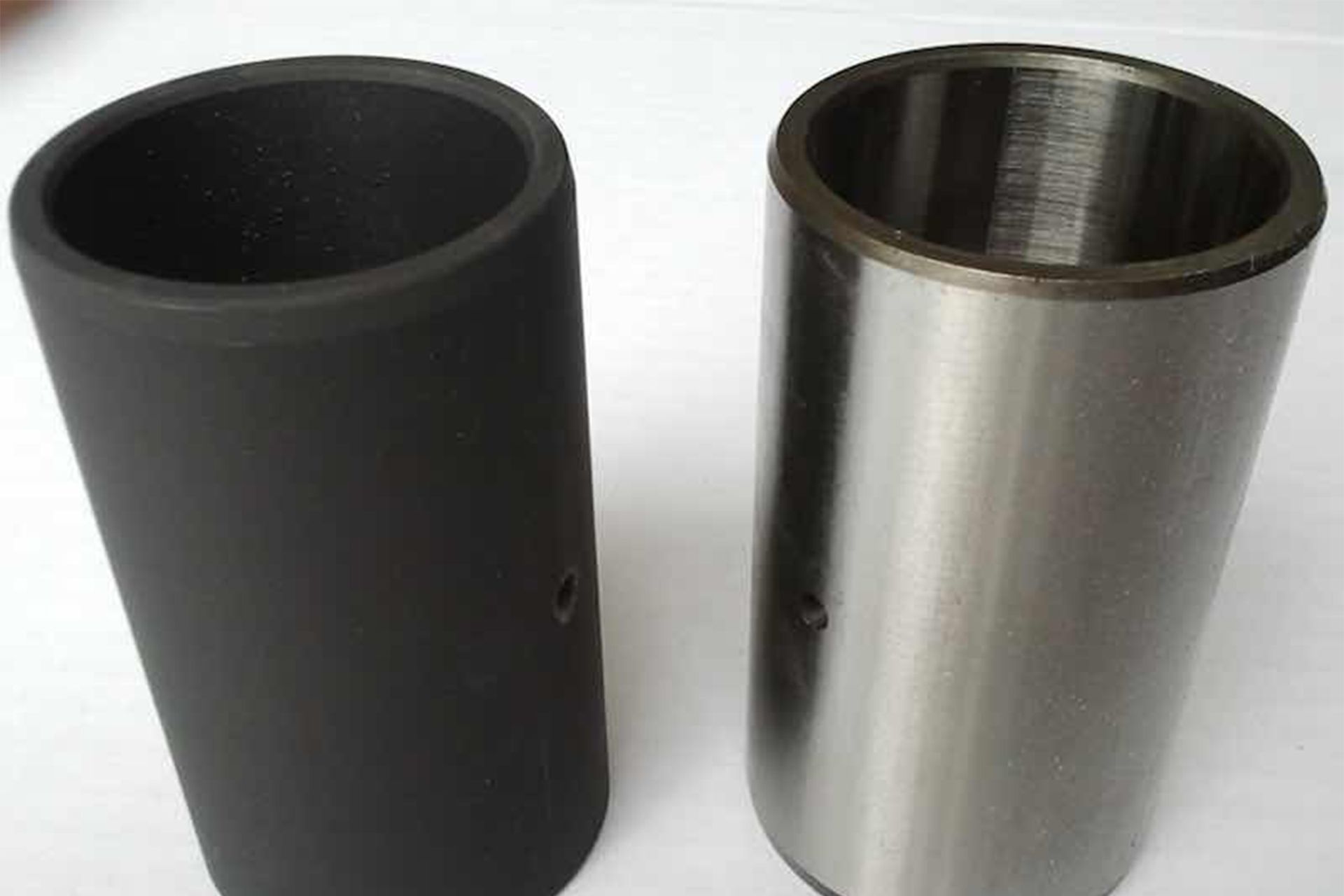
Nitride vs. Phosphate Finishes: Differences & Considerations
When it comes to crafting firearms, every detail matters. The choice of finish for firearm components isn’t just a technical decision; it’s a critical factor that can determine the reliability, performance, and lifespan of these precision machined parts. Two options stand out in the quest for the ideal finish: phosphate and nitride.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the practical differences between these finishes, providing businesses and manufacturers with valuable insights to empower their choices regarding enhancing the durability and functionality of their firearm components.
Benefits of Phosphate Finish
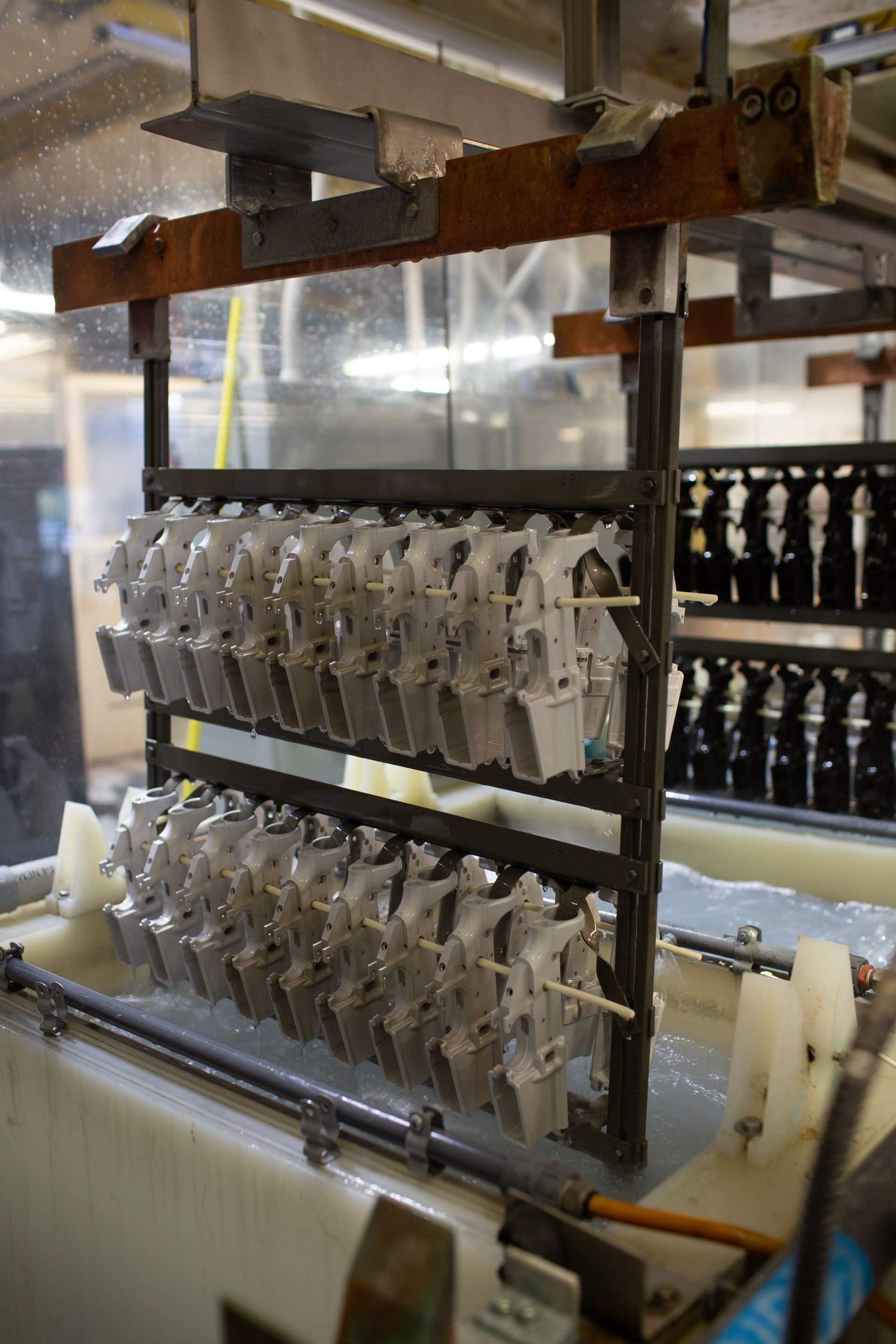
The Manganese phosphate finish, also known as phosphate coating or Parkerizing, is an essential staple in the firearm industry for several compelling reasons:
- Mil-Spec Compliance: Phosphate finishes adhere to strict specifications, ensuring high-quality and standardized results for military parts.
- Enhanced Lubrication: The surface of phosphate coating allows for oil to seep into the pores, creating a lubricating layer between the metal surface and external elements, which exhibits excellent lubricity, a critical factor in ensuring the reliable function of firearms.
- Adhesion Properties: Phosphate finishes offer excellent adhesion, making them compatible with additional coatings or treatments, further enhancing firearm performance.
- Aesthetic Appearance: The dark or black appearance achieved with manganese phosphate finishes not only serves an aesthetic purpose but can also be desirable for camouflage or tactical considerations, especially in firearms and military applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For manufacturers, phosphate finishing is a cost-effective solution without compromising quality.
Benefits of Nitride Finish
On the other hand, nitride finishes bring their own set of advantages to the table:
- Hardness: Nitride finishes, such as nitrocarburizing or melonite, create a hard, wear-resistant surface by diffusing nitrogen into the metal. This quality significantly improves the material's hardness, making it more resistant to scratching, abrasion, and general wear and tear.
- Corrosion Resistance: Nitride finishes provide good corrosion resistance, although not as high as manganese phosphate. The nitrogen-enriched surface creates a protective barrier against rust and other corrosive elements, making it suitable for applications where hardness and corrosion resistance are important.
- Improved Fatigue Strength: Nitriding can enhance the fatigue strength of metal components, which is extremely valuable when parts endure repetitive stress or cyclic loading.
- Minimal Dimensional Changes: Nitriding processes generally result in minimal dimensional changes to treated metal, proving advantageous for precision components by maintaining tight tolerances and eliminating the need for additional machining or finishing operations.
- Reduced Friction: The nitriding process can yield a smoother surface finish, reducing friction between moving parts and contributing to improved reliability, performance, and overall accuracy of firearms.
Cost Comparison
When it comes to cost-effectiveness, phosphate finishes take the spotlight. Their simplicity and efficiency in the application process make them a much more affordable option than nitride finishes. The straightforward nature of phosphate finishing not only helps manufacturers control costs but also ensures that businesses can maintain high-quality standards without straining their financial resources.
Corrosion Resistance
When evaluating firearm finishes, it’s essential to consider their performance in the face of various environmental challenges, including humidity, salt spray, and chemical exposure. The maritime or coastal regions experience some of the most demanding circumstances that a metal finish can face with exposure to saltwater and corrosive elements. In these environments, Manganese phosphate coatings are generally preferred.
- High Corrosion Resistance: Manganese phosphate coatings offer outstanding corrosion resistance, specifically against rust and oxidation, making them ideal for safeguarding metal components in marine environments where the threat of saltwater corrosion is prominent.
- Effective Barrier: The phosphate layer formed during the manganese phosphate process acts as a barrier, creating a protective shield that helps prevent saltwater and other corrosive agents from directly contacting the metal surface. This barrier is crucial for slowing down the corrosion process and extending the lifespan of the treated components.
- Adhesion to Metal: Manganese phosphate has good adhesion to the metal substrate, ensuring the protective coating remains intact even in abrasive saltwater conditions.
- Lubricating Properties: The natural lubricating properties of manganese phosphate can contribute to smoother operation of metal components, reducing friction and wear, which is beneficial in marine applications.
- Proven Performance: Manganese phosphate finishes have a track record of effective performance in marine environments and are commonly used for protecting firearms and other metal objects exposed to saltwater conditions.
While nitride finishes, such as nitrocarburizing or melonite, offer increased hardness and wear resistance advantages, they may not provide the same level of corrosion resistance as manganese phosphate in marine settings. Nitride finishes can still be suitable for marine applications, especially where wear resistance is a primary concern. However, additional measures may be needed to address the corrosion challenges posed by saltwater.
Wear Resistance
Nitride finishes, known for their exceptional hardness, hold a significant advantage when it comes to wear resistance.
- Increased Hardness: Nitride finishes significantly increase the surface hardness of the treated metal. The process involves diffusing nitrogen into the material, creating a hard and wear-resistant layer. This hardness makes components more resistant to abrasion and wear.
- Wear Resistance: The hard surface created through nitriding offers exceptional wear resistance and is particularly beneficial in applications where components undergo friction, sliding, or other forms of mechanical wear.
- Reduced Friction: Nitride finishes contribute to reduced friction between moving parts. This reduction in friction enhances wear resistance and results in smoother operation and improved overall performance.
- Improved Fatigue Strength: Nitriding can enhance the fatigue strength of metal components, making them more resistant to wear and failure under repetitive stress or cyclic loading conditions.
- Minimal Dimensional Changes: Nitriding processes typically involve minimal dimensional changes to the treated metal, which is beneficial for precision components where maintaining tight tolerances is essential.
Choosing the Right Finish
Ultimately, the choice between phosphate and nitride finishes depends on various factors, including the intended use of the firearm components and the budget considerations of the manufacturer. Consult with the metal finishers at Light Metals Coloring to make an informed decision tailored to your specific needs.
Phosphate and nitride finishes have unique advantages, and the selection should align with the intended application and performance requirements. For more information on
metal finishing services tailored to firearm businesses and manufacturers, including
manganese phosphate options, explore the expertise of Light Metals Coloring.