A Guide to Chemical Conversion Coatings
Chemical conversion coatings are essential to provide a protective layer on metal surfaces, enhancing their corrosion resistance and longevity. These coatings are widely utilized in various industries, such as aerospace, firearms, and military applications. This guide will cover three conversion coating types: chromate, phosphate, and black oxide.
Whether you are using aluminum or steel alloys, understanding the properties of each coating process can ensure you are selecting the appropriate solution for your needs.
Chromate Conversion Coatings
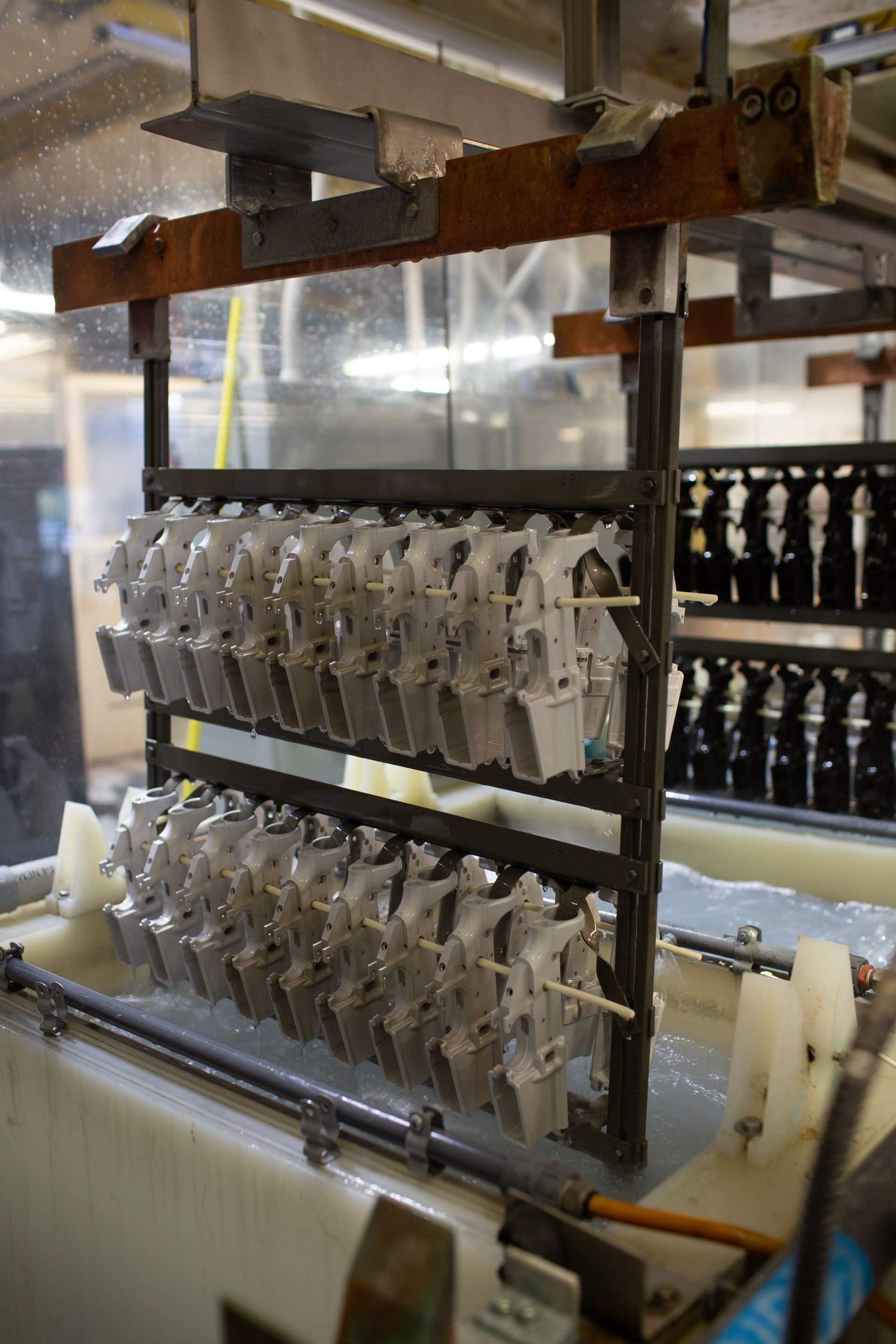
Chromate conversion coating is a chemical process that forms a protective layer on aluminum and other metals, providing enhanced corrosion resistance, improved paint adhesion, and a decorative finish. This coating is achieved by immersing metal parts in a solution containing hexavalent or trivalent chromates. You may encounter these coatings while exploring LMC’s anodizing services for aluminum parts. This process has various features and applications, with several coatings available.
Features
Chromate conversion coatings offer a variety of benefits to metal parts. Some key features include:
- Enhanced corrosion resistance, which prevents parts from deteriorating due to exposure to harsh environments
- Improved paint adhesion, ensuring proper bonding between the paint and metal surface, reducing the risk of peeling or chipping
- Electrical conductivity, making it suitable for use in electronic applications
- A decorative finish, providing an aesthetically pleasing appearance
Applications
Chromate conversion coatings can be used in various industries and applications, such as:
- Aerospace: For protection of aircraft components against harsh environmental conditions
- Automotive: To improve the performance and longevity of metal parts
- Electronics: For printed circuit board assemblies and other electronic components that require conductivity
- Construction: To enhance the durability of aluminum structures and components
Types of Chromate Conversion Coatings
Different chromate conversion coatings have distinct chemical compositions and forms. Type 1 and Type 2 of the MIL-DTL-5541 standard are the primary types of chromate conversion coatings:
- Type 1: Hexavalent chromates, which provide a high level of corrosion resistance but are less environmentally friendly due to the presence of toxic substances.
- Type 2: Trivalent chromates offer similar corrosion protection but are considered more environmentally friendly since they contain fewer toxic chemicals.
Chromate Conversion Coating vs. Anodizing
While both chromate conversion coatings and anodizing processes aim to improve the corrosion resistance of metal surfaces, they differ in several aspects:
- Chromate conversion coatings form a thinner layer on metal surfaces, while anodizing creates a thicker, harder layer that also penetrates the base aluminum.
- Anodizing changes the metal surface structure, whereas chromate conversion coatings do not alter the metal's underlying structure.
- Anodizing provides a broader range of colors and finishes than chromate conversion coatings.
- Chromate conversion coatings offer electrical conductivity whereas anodizing insulates the aluminum from conducting current, making them more suitable for electronic applications.
- Chromate conversion is typically a more cost effective finish than anodize when only being used as a base for other coatings such as painting or powder-coating.
Phosphate Conversion Coatings
Phosphate conversion coating is a chemical treatment process applied to metal surfaces to create a protective layer that enhances corrosion resistance, improves paint adhesion, and minimizes wear. This coating is formed by the reaction between the metal surface and the phosphate solution, resulting in an adhesive crystalline coating.
Features
Phosphate conversion coatings offer you several valuable features such as:
- Enhanced corrosion resistance: The coating forms a barrier that protects the underlying metal from oxidation and corrosion.
- Improved paint adhesion: The rough surface texture created by the coating generates increased surface area, promoting the bonding of paint or other coatings.
- Reduced metal-to-metal friction: Phosphate coatings create a lubricated surface, minimizing wear and galling in sliding contact applications.
Applications
You can benefit from the use of phosphate conversion coatings in various applications across industries, such as:
- Automotive: To protect engine components, chassis, and other parts from corrosion and wear.
- Aerospace: For corrosion prevention on aluminum, magnesium, and other light alloy parts.
- Construction: For corrosion protection and paint adhesion on structural steel, pipe systems, and metal fasteners.
- Electronics: For printed circuit boards, switches, and connectors, ensuring better electrical contact.
- Firearms and Defense: For Corrosion prevention from wear and outdoor elements, to enhance the functionality and for aesthetics.
Types of Phosphate Conversion Coatings
There are several types of phosphate conversion coatings available to suit your specific requirements:
- Zinc Phosphate: Known for its excellent corrosion protection and strong paint adhesion properties, it is widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
- Iron Phosphate: A lighter and more environmentally friendly coating option, providing corrosion resistance and enhancing paint adhesion in applications like appliance manufacturing and metal finishing.
- Manganese Phosphate: Used primarily to reduce friction in sliding component applications like bearings, gears, and engine components. Manganese phosphate coatings improve wear resistance and have excellent oil absorption properties.
By understanding the features, applications, and types of phosphate conversion coatings, you can choose the most suitable solution for your metal finishing needs to enhance performance, appearance, and durability.
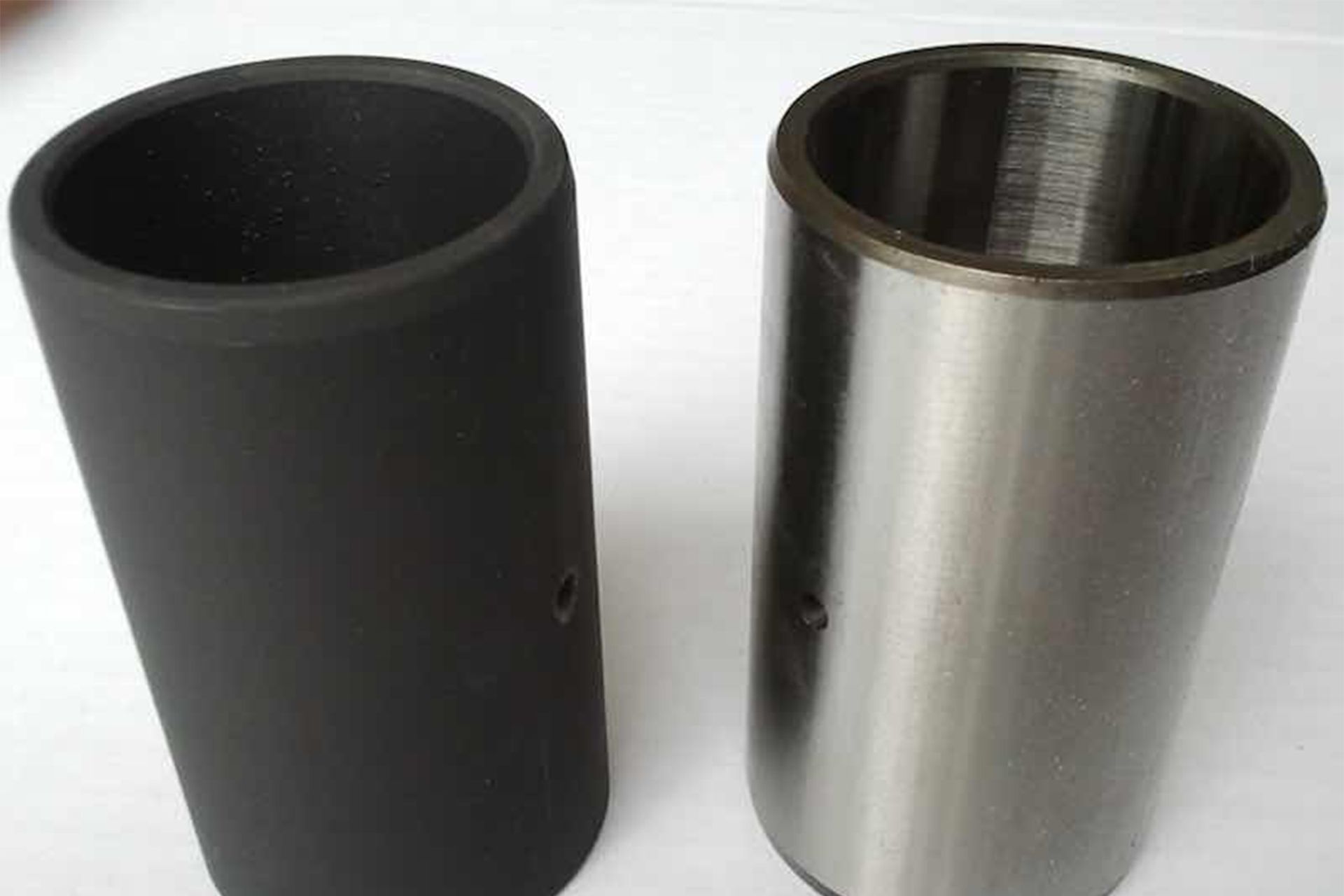
Black Oxide Coatings
Black oxide coatings are a type of chemical conversion coating applied to various metals to provide a black, protective surface. This finish enhances the metal's appearance and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
Features
The main features of black oxide coatings include increased corrosion resistance, minimal dimensional changes, and improved aesthetics. The process does not leave a significant buildup on the surface of the metal, ensuring that the original dimensions remain largely unaffected. Additionally, the black matte finish offers an attractive and professional appearance.
Applications
The use of black oxide coatings spans across numerous industries, with some common applications including:
- Automotive components: To protect against rust and improve the appearance of parts like engine components, bolts, and fasteners.
- Firearms: To enhance various firearm components' durability, performance, and appearance.
- Tooling and equipment: To improve the wear resistance and longevity of cutting tools, gears, and other machine parts.
- Architectural hardware: To protect and enhance the look of door handles, hinges, and other fixtures.
Types of Black Oxide Coatings
There are different types of black oxide coatings available, suitable for various metals and applications:
- Hot black oxide: This process uses a heated alkaline solution to form a black oxide layer on steel and iron. Hot black oxide is the most common type and offers the best corrosion resistance.
- Cold black oxide: Suitable for applications that cannot withstand the high temperatures of the hot black oxide process, such as those with temperature-sensitive components. Cold black oxide typically provides less corrosion resistance and has a shorter lifespan than hot black oxide.
- Black oxide for stainless steel: A slightly different process tailored specifically for stainless steel parts, which enhances their corrosion resistance and appearance.
- Black oxide for light metals: A specialized process designed for aluminum, titanium, and other light metals, providing a black oxide coating with a similar range of benefits to steel and iron.
Black oxide coatings offer various advantages for metal components, with different types catering to the specific needs of various applications. You can rely on professionals like Light Metals Coloring to help select and apply the optimal black oxide coating for your project.
How to Choose the Right Coating
When selecting a chemical conversion coating, it’s crucial to tailor your choice to the specific needs of your project. This involves considering several key factors:
- Identify the Purpose: Start by understanding the intended use of your metal components. Whether they’re for structural, decorative, or functional applications will influence your choice of coating.
- Evaluate Desired Properties: Different coatings come with various advantages, such as resistance to wear, enhanced durability, or thermal insulation. Make a list of the properties that are most important for your project.
- Assess Protection Requirements: Consider the environmental conditions your metal parts will be exposed to. This could range from moisture and chemical exposure to high or low temperatures. Choose a coating that offers the level of protection needed for these conditions.
Consult the experienced team at LMC for expert guidance in selecting the ideal coating for your needs. We’ll ensure your metal parts perform well, maintain their appearance, and meet your unique needs.